The means through which data is transformed from one place to another is called transmission or communication media. There are two categories of transmission media used in computer communications.
- BOUNDED/GUIDED MEDIA
- UNBOUNDED/UNGUIDED MEDIA
BOUNDED/GUIDED MEDIA
Bounded media are the physical links through which signals are confined to narrow path. These are also called guide media. Bounded media are made up o a external conductor (Usually Copper) bounded by jacket material. Bounded media are great for LABS because they offer high speed, good security and low cast. However, some time they cannot be used due distance communication. Three common types of bounded media are used of the data transmission. These are
- Coaxial Cable
- Twisted Pairs Cable
- Fiber Optics Cable
Coaxial
Cable
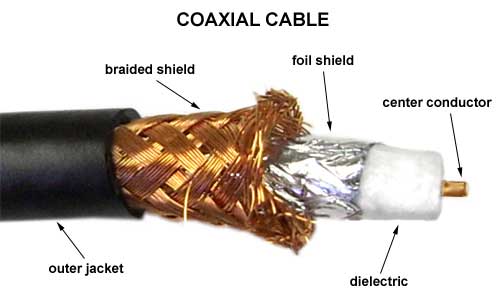
Coaxial cable is very common & widely used commutation media. For example TV wire is usually coaxial.
Coaxial cable gets its
name because it contains two conductors that are parallel to each other. The
center conductor in the cable is usually copper. The copper can be either a
solid wire or stranded martial.
Outside this central
Conductor is a non-conductive material. It is usually white, plastic material
used to separate the inner Conductor form the outer Conductor. The other
Conductor is a fine mesh made from Copper. It is used to help shield the cable
form EMI.
Outside the copper
mesh is the final protective cover. (as shown in Fig)
The actual data
travels through the center conductor in the cable. EMI interference is caught
by outer copper mesh. There are different types of coaxial cable vary by gauge
& impedance.
Gauge is the measure
of the cable thickness. It is measured by the Radio grade measurement, or RG
number. The high the RG number, the thinner the central conductor core, the
lower the number the thicker the core.
CHARACTERISTICS OF
COAXIAL CABLE
·
Low cost
·
Easy to install
·
Up to 10Mbps capacity
·
Medium immunity form
EMI
·
Medium of attenuation
ADVANTAGES COAXIAL CABLE
·
Inexpensive
·
Easy to wire
·
Easy to expand
·
Moderate level of EMI
immunity
DISADVANTAGE COAXIAL
CABLE
·
Single cable failure
can take down an entire network
Twisted Pair Cable
The most popular network cabling is Twisted pair. It is light weight, easy to install, inexpensive and support many different types of network. It also supports the speed of 100 mps.Twisted pair cabling is made of pairs of solid or stranded copper twisted along each other. The twists are done to reduce vulnerably to EMI and cross talk. The number of pairs in the cable depends on the type. The copper core is usually 22-AWG or 24-AWG, as measured on the American wire gauge standard. There are two types of twisted pairs cabling :
- Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
- Shielded twisted pair (STP)
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
UTP is more common. It can be either voice grade or data grade depending on the condition. UTP cable normally has an impedance of 100 ohm. UTP cost less than STP and easily available due to its many use.
Characteristics of UTP
- low cost
- easy to install
- High speed capacity
- High attenuation
- Effective to EMI
- 100 meter limit
Advantages of UTP
- Easy installation
- Capable of high speed for LAN
- Low cost
Disadvantages of UTP
- Short distance due to attenuation
Shielded twisted pair (STP)
It is similar to UTP but has a mesh shielding that’s protects it from EMI which allows for higher transmission rate.
Characteristics of STP
- Medium cost
- Easy to install
- Higher capacity than UTP
- Higher attenuation, but same as UTP
- Medium immunity from EMI
- 100 meter limit
Advantages of STP:
- Shielded
- Faster than UTP and coaxial
Disadvantages of STP:
- More expensive than UTP and coaxial
- More difficult installation
- High attenuation rate

Fiber
Optics
Characteristics Of
Fiber Optic Cable:
·
Expensive
·
Very hard to install
·
Capable of extremely
high speed
·
Extremely low
attenuation
·
No EMI interference
Advantages Of Fiber
Optic Cable:
·
Fast
·
Low attenuation
·
No EMI interference
Disadvantages Fiber
Optics:
·
Very costly
·
Hard to install

UNBOUNDED/UNGUIDED MEDIA
Unguided media relates to data transmission through the air and is commonly referred to as wireless. The transmission and reception of data is carried out using antenna.
There are two main ways that antenna work:
- Directional (in a beam)
- Omnidirectional (all around)
2.0 Communication Devices
A
communication device is a peripherical used for communication between the
computers and other devices. Modem is a popular communication device which is
normally used for internet communication. Infra red, Bluetooth and LAN card are
the examples of communication devices.
Modem
The Modem is a hardware device
that enables a computer to send and receive information
over telephone lines by converting the digital data used by
your computer into an analog signal used on phone lines and then
converting it back once received on the other end. In the below picture, is an
example of an internal expansion card modem.Modems are referred to as an asynchronous
device, meaning that the device transmits data in an intermittent stream of
small packets. Once received, the receiving system then takes the data in the
packets and reassembles it into a form the computer can use.

Infrared
Definition: Infrared technology allows computing devices to communicate via short-range wireless signals. With infrared, computers can transfer files and other digital data bidirectionally. The infrared transmission technology used in computers is similar to that used in consumer product remote control units.
nstallation and Usage - Computer infrared network adapters both transmit and receive data through ports on the rear or side of a device. Infrared adapters are installed in many laptops and handheld personal devices. In Microsoft Windows, infrared connections can be created through the same method as other local area network connections. Infrared networks were designed to suppport direct two-computer connections only, created temporarily as the need arises. However, extensions to infrared technology also support more than two computers and semi-permanent
Performance - Infrared technology used in local networks exists in three different forms:
- IrDA-SIR (slow speed) infrared supporting data rates up to 115 Kbps
- IrDA-MIR (medium speed) infrared supporting data rates up to 1.15 Mbps
- IrDA-FIR (fast speed) infrared supporting data rates up to 4 Mbps
Bluetooth
Definition: Bluetooth is a specification (IEEE 802.15.1) for the use of low-power radio communications to link phones, computers and other network devices over short distances without wires. Bluetooth technology was designed primarily to support simple wireless networking of personal consumer devices and peripherals, including cell phones, PDAs, and wireless headsets. Wireless signals transmitted with Bluetooth cover short distances, typically up to 30 feet (10 meters). Bluetooth devices generally communicate at less than 1 Mbps.
Bluetooth networks feature a dynamic topology called a piconet or PAN. Piconets contain a minimum of two and a maximum of eight Bluetooth peer devices. Devices communicate using protocols that are part of the Bluetooth Specification. Definitions for multiple versions of the Bluetooth specification exist including versions 1.1, 1.2 and 2.0.

No comments:
Post a Comment